20230117日志
2023年1月17日
golang #
进制 #
0b123
0o123
0x123
溢出 #
// inc
func inc(a int) int {
if a == math.MaxInt {
panic("int overflow")
}
return a+1
}
func inc(a int32) int32 {
if a == math.MaxInt32 {
panic("int32 overflow")
}
return a + 1
}
// add
func add(a int, b int) int {
if a > math.Maxint - b {
panic("int add overflow")
}
return a + b
}
// multiple
func multiplyInt(a, b int) int {
if a == 0 || b == 0 {
return 0
}
result := a * b
if a == 1 || b == 1 {
return result
}
if a == math.MinInt || b == math.MinInt {
panic("int overflow")
}
if result/b != a {
panic("int overflow")
}
return result
}
浮点数 #
- 在有限位数内比较
- 在有加法与乘法运算,优先乘法运算保证更高精度
理解length和capcity #
- 在1024之前双倍增加,之后增加25%
- 切片的长度为切片表达式的长度,容量为剩余的capcity, 填满之后创建新的切片
s1 := make([]int, 3, 6) // len 3, cap 6
s2 := s1[1:3] // len 2, cap 5
s1[1] = 1
s2 = append(s2, 2)
// s1 010 len 3, cap 6
// s2 102 len 4, cap 5
s2 = append(s2, 3, 4, 5)
// s1 010 len 3, cap 6
// s2 102345 len 6, cap 10
构建切片 #
在make创建切片时,赋予合适的长度,容量
理解nil和empty #
var s []string // empty, nil
s = []string(nil) // empty, nil, 一般不使用,与第一种不同是可以写在一行
s = []string{} // empty, not nil, 一般不使用, 采用方法一
s = make([]string, 0) // empty, not nil, 知道未来的长度时采用这种
- nil不需要allocate, empty需要
- nil也可以append
- reflect.DeepEqual 下 nil和empty不同, encoding/json序列化的结果也不同
检查切片 #
- len(nil) == 0
- len(empty) == 0
copy slice #
copy时设置 len 避免多余的allocate
append 的副作用 #
s1 := []int{1, 2, 3}
s2 := s1[1:2]
s3 := append(s2, 10)
// 解决方案
// 1. copy
// 2. full slice, s2 := s1[1:2:1], 指定cap为1
slice 导致的内存泄漏 #
capcity 泄漏 #
s1 := []int{1, 2, 3 ...}
s2 := s1[1:2]
// 如果s1很长, s2会保留s1剩余的capcity
方案: copy, copy会复制源和目的最小的长度
slice pointer 泄漏 #
如果一个slice的element是pointer或有pointer字段的struct, 元素不会被gc清理
- copy
- 切片后剩余内容置为 nil
map 初始化 #
map 通过hash函数确定切片索引位置,值指向bucket链表的头部
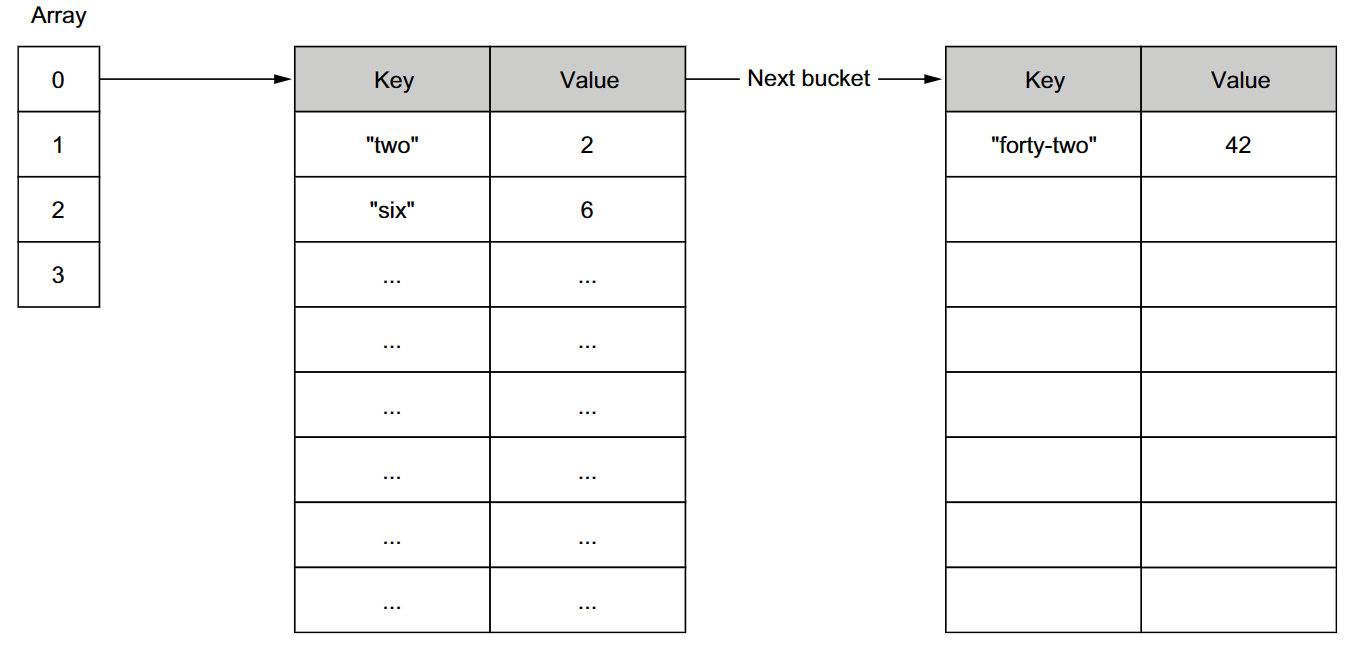
map grow
- 每个bucket可以存储8个键值对
- buckets 的平均数量超过了 load factor 6.5
- 过多的 bucket 满了
// n 表示n个元素
make(map[string]int, n)
map 内存泄漏 #
make(map[int][128]byte)map添加100万key,然后全部删除, 内存不会全部释放,因为分配的bucket不是释放
- 在 peace time重建map
- map的值存储指针, 不会减少bucket的数量,但是会将, bucket中每个entry的占用减少
- 如果key或value超过128byte,不会直接存在bucket中,存储一个指针
不正确的比较 #
== 和 != 不能用于比较 slice 和 map
- Boolean: Compare whether two Booleans are equal.
- Numerics(int, float, and complex types): Compare whether two numerics are equal.
- Strings: Compare whether two strings are equal.
- Channels: Compare whether two channels were created by the same call to make or if both are nil.
- Interfaces: Compare whether two interfaces have identical dynamic types and equal dynamic values or if both are nil.
- Pointers: Compare whether two pointers point to the same value in memory or if both are nil.
- Structs and arrays: Compare whether they are composed of similar types.
- 使用 reflect.DeepEqual 比较slice, map, struct, 注意 nil 和 empty的不同, 比 == 慢100倍