20230116日志
2023年1月16日
golang #
string是utf8编码的,底层存储的是1-4个字节
s := "hello"
fmt.Println(len(s)) // 5
s := "汉"
fmt.Println(len(s)) // 3
string的正确遍历方式
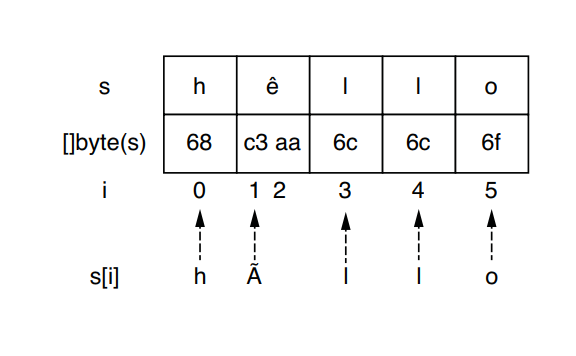
s := "hêllo"
for i := range s {
fmt.Printf("position %d:%c\n", i, s[i])
}
0, h
1, Ã
3, l
4, l
5, o
for i, r := range s {
fmt.Printf("position %d:%c\n", i, c)
}
0, h
1, ê
3, l
4, l
5, o
字符串内存布局
string,TrimRight 与 TrimSuffix的区别
string在代码接口设计时中更应该考虑 []byte类型
string拼接使用 sb:=strings.Builder(), sb.grow()
string切片默认是共享原字符串, 使用strings.copy(a[:3]), 或者 string([]byte(a[:3])), 防止内存泄漏
算法 #
使用记数排序法解决h指数问题
英语 #
独立主格 两个句子,不同主语(),从句使用独立主格
- 名词+现在分词
- the wolf inviting him, …
- 名词+过去分词
- a carrot held in the hand
- 名词+动词不定式
- The rabbit to come, the wolf is overjoyed
- 名词+名词
- Many animals went to the party, some of them rabbits and wolves
- 名词+形容词
- Many animals went to the party, some of them happy
- 名词+副词
- The rabbit sat on a chair, head down
- 名词+介词短语
- The rabbit came in, carrot in hand